Composition of Urine and its Significance
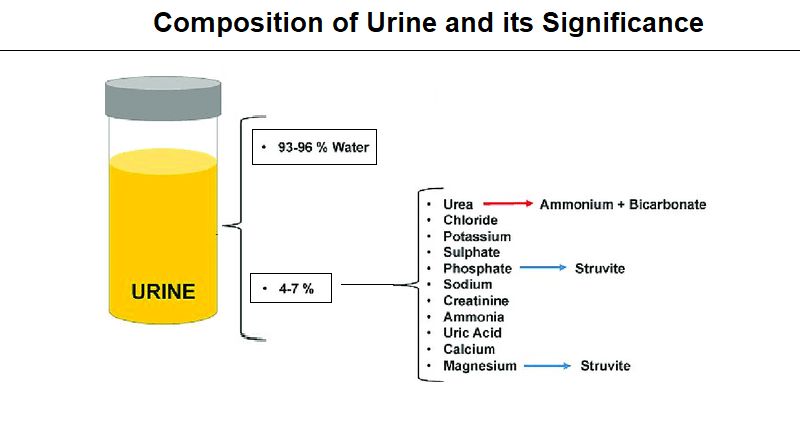
Urine is a fluid that the body excretes to eliminate waste and excess substances, where water is the main part of urine composition. additionally, it contains other substance such as urea, creatinine, ammonia, and inorganic salts. The composition of urine can be influenced by a variety of factors including age, gender, race, diet, medications, and exercise. A change in urine composition can indicate the presence of a medical condition, making urine analysis an important diagnostic tool.
Reasons for Urine Tests
A urine test can be recommended for several reasons, including routine health maintenance, hospital admission, suspicion of a medical condition, and monitoring ongoing ailments. The following are some of the symptoms that warrant a urine test:
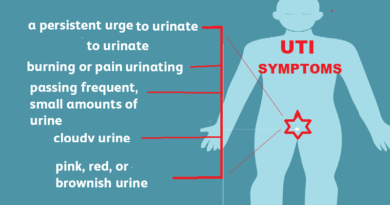
- Pain or discomfort during urination (dysuria)
- Red, pink, or brown urine color (hematuria)
- Foul odor in urine
- Cloudy urine
- Abdominal pain
- Back pain
A urine test is also recommended to screen for medical conditions such as urinary tract infections, kidney disease, liver disease, diabetes, hypertension, dehydration, gout, and more. Other urine tests include pregnancy tests, toxicology screens, STI screening, and pregnancy health monitoring.
Frequency of Urine Excretion
On average, an adult excretes urine about 8 times a day. This frequency can be influenced by the amount of fluid consumed, the overall diet, and other factors. Pregnant women and the elderly often excrete urine more frequently than others. However, excessive and frequent urination can also indicate the presence of medical conditions such as urinary tract infections, kidney disease, enlarged prostate, vaginitis, and interstitial cystitis, and require a visit to a primary care physician.
Liver Problems and Urine Color
Liver problems can cause increased levels of direct bilirubin in the bloodstream, which is then excreted via urine. A high bilirubin concentration in urine can change its color, making it a darker brown or tea-colored.
Smelly Urine
Foul-smelling urine can indicate a variety of issues, including dehydration, multivitamin intake, urinary tract infections, kidney disease, uncontrolled blood sugar in diabetics, and consumption of certain foods such as asparagus.
Conclusion
It is important to maintain regular health visits with a healthcare provider to ensure good health. If you notice any changes in your urine, such as the color, odor, or frequency, it is essential to seek medical advice. Your healthcare provider may perform a urine test to better understand your health and determine if further testing is needed. Early detection and treatment of any medical conditions can help prevent complications and promote a healthy, active lifestyle.
SOURCES