Vitamin B12 and Red Blood Cell Formation: Why It Matters
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a vital nutrient that plays a crucial role in various body functions including the formation of red blood cells. In this article, we will explore why vitamin B12 is essential for red blood cell formation, the consequences of vitamin B12 deficiency, food sources of vitamin B12, the importance of supplements, and tips for incorporating more vitamin B12 into your diet.
1. The Role of Vitamin B12 in Red Blood Cell Formation
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that plays a critical role in the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow. Red blood cells are responsible for carrying oxygen to different parts of the body, and without adequate levels of vitamin B12, the production of these cells can be affected, leading to anemia.
Vitamin B12 helps to create healthy red blood cells by facilitating DNA synthesis, which is needed for the proper maturation and division of red blood cells. This means that vitamin B12 is necessary for the formation of new red blood cells and for the maintenance of healthy existing ones.
In addition, vitamin B12 also helps to maintain the proper size and shape of red blood cells, which is important for their ability to carry oxygen effectively. Without vitamin B12, red blood cells can become larger and more oval-shaped, making it harder for them to squeeze through small blood vessels and deliver oxygen to the body’s tissues.
In addition to promoting red blood cell formation, vitamin B12 is also necessary for the formation of white blood cells and platelets [3]. Vitamin B12 is also involved in cell metabolism, nerve function, and the production of DNA, which carries genetic information in cells [2].
2. The Consequences of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to anemia, a condition characterized by a lack of healthy red blood cells in the body. This can lead to fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, and other symptoms. Long-term vitamin B12 deficiency can also cause nerve damage, leading to tingling and numbness in the hands and feet, difficulty with balance, and other neurological symptoms.
vitamin B12-deficiency anemia
A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to a type of anemia called vitamin B12-deficiency anemia, which occurs when the body doesn’t have enough vitamin B12 to make healthy red blood cells [1]. Vitamin B12 is necessary for the production of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. Without enough vitamin B12, the red blood cells can’t carry oxygen effectively, resulting in anemia [2].
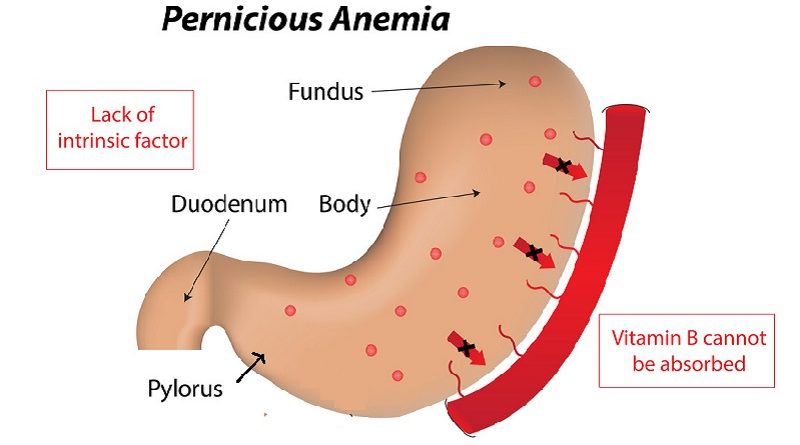
Pernicious anemia
Pernicious anemia is a type of vitamin B12-deficiency anemia that occurs when the body can’t absorb vitamin B12 properly due to a lack of intrinsic factor, a protein produced by the stomach that is necessary for vitamin B12 absorption.
3. Food Sources of Vitamin B12 for Red Blood Cell Formation
Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal-based foods, such as meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products. Plant-based sources of vitamin B12 are limited, but fortified breakfast cereals and nutritional yeast can also provide a source of this essential nutrient. Incorporating more of these foods into your diet can help ensure you have enough vitamin B12 to support red blood cell formation. [2][4]
If you’re at risk of a vitamin B12 deficiency, such as if you’re a vegan or vegetarian or have a digestive disorder that impairs absorption of nutrients, it may be necessary to take a vitamin B12 supplement or receive B12 injections [4].
4. The Importance of Vitamin B12 Supplements
For individuals who do not consume enough vitamin B12 through their diet, supplements can be a valuable way to ensure they get the recommended daily intake of this essential nutrient. Vitamin B12 supplements are available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and injections.
5. Tips for Incorporating More Vitamin B12 into Your Diet
- Include more animal-based foods in your diet, such as meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products.
- Choose fortified breakfast cereals and nutritional yeast, which can provide a source of vitamin B12 for individuals following a plant-based diet.
- Consider taking a vitamin B12 supplement if you are at risk of deficiency or do not consume enough through your diet.
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Importance of Vitamin B12 | Essential for the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow |
| Role in Red Blood Cell Formation | Helps create healthy red blood cells by facilitating DNA synthesis |
| Role in Maintaining Proper Red Blood Cell Size and Shape | Necessary for effective oxygen transportation |
| Consequences of Deficiency | Can lead to vitamin B12-deficiency anemia and other health problems |
SUMMARY
Vitamin B12 plays a vital role in promoting red blood cell formation, which is essential for carrying oxygen throughout the body. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to anemia and other health problems. By incorporating more vitamin B12-rich foods into your diet, taking supplements if necessary, and talking to your healthcare provider, you can ensure you have enough vitamin B12 to support red blood cell formation and maintain optimal health.
SOURCES
[1] https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/vitamin-b12-deficiency-anemia
[2] https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements-vitamin-b12/art-20363663
[3] https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/anemia/vitamin-b12-deficiency-anemia
[4] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/vitamin-b12-benefits