Definitive HIV Testing After Three Months: Understanding the Window Period
Is HIV Testing After Three Months Definitive? This is a common question, repeatedly asked by worried persons exposed to infection with HIV. In this article, we will discuss the accuracy and timing of HIV tests conducted three months after potential exposure. And we explore, in short, the most popular HIV test types. Here’s a detailed overview:
Timing and Reliability of HIV Testing
HIV testing is crucial for early diagnosis and ensuring accurate results. While it’s possible to detect 95% of HIV infections four weeks post-exposure, a confirmatory test at three months (90 days) post-exposure is recommended to ensure the negative result is definitive. This confirmation is vital, when the initial test result is negative, it helps rule out any false negatives due to the window period issues.
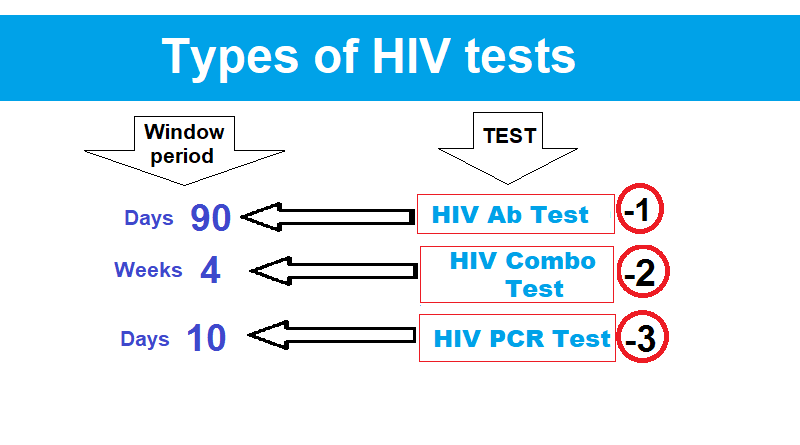
Types of HIV Tests and Their Window Periods
- HIV Antibody Test:
- This is the most common type of HIV test.
- Antibodies can typically be detected within 3-12 weeks post-exposure.
- After 90 days, this test provides a conclusive negative result.
- Antigen/Antibody Test (Combo Test):
- This test can detect HIV earlier, within 2-6 weeks post-exposure, by identifying antibodies and antigens (such as p24, a protein in the virus).
- p24 usually appears in the blood of infected persons earlier than the antibodies.
- Due to looking for antigen p24, it offers a shorter window period.
- Nucleic Acid Test (NAT) / RNA / PCR:
- It detects the virus’s genetic material (RNA).
- It can identify HIV as early as 6-10 days post-exposure.
- Despite its early detection capability, it is costly and not widely available.
- It is generally reserved for high-risk exposures or persons with early suggestive symptoms.
Dr. Helal’s Recommendations
Dr. Helal emphasizes the importance of using the antibody test for its reliability and accessibility. He advises against unnecessary tests, which can be more expensive and less available.
Conclusion
If you suspect exposure to HIV, it’s essential to undergo a Definitive HIV Testing. You can do initial HIV antibody test after about four weeks, and a follow-up test at 90 days for a conclusive result. If both tests are negative, you can be confident that you are not infected, provided no further exposures occur.