STDs in the Philippines: Understanding
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) remain a significant public health issue globally, including in the Philippines. Despite efforts to mitigate their spread, challenges such as stigma, limited access to healthcare, and lack of education persist. This blog delves into the prevalence, impact, and efforts to address STDs in the Philippines, guided by insights from various sources, including the comprehensive review provided by Hello Doctor.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- HIV/AIDS: An Ongoing Challenge
- Common Curable STDs
- Gender Disparities in STD Detection
- Access to Testing and Treatment
- Public Health Efforts and Education
- Summary
1. About STDs in the Philippines
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections passed from one person to another through sexual contact. They can have severe health implications if left untreated, including infertility, organ damage, and increased susceptibility to other infections. The stigma associated with STDs often prevents individuals from seeking timely medical help, exacerbating the spread and impact of these infections.
In the Philippines, the discussion around STDs has traditionally been taboo, but there has been a shift towards more open discussions and proactive health measures. This blog aims to highlight the current state of STDs in the Philippines, focusing on the most common infections, challenges in detection, and efforts to improve healthcare access and education.
2. HIV/AIDS: An Ongoing Challenge
HIV Prevalence and Statistics
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) continues to be a significant public health issue in the Philippines. According to the Department of Health (DOH), the number of reported HIV cases has been steadily increasing over the years. From 1984 to 2017, over 44,000 cases were reported, and the numbers continue to rise alarmingly. In 2008, the average number of newly diagnosed HIV cases per day was just one. By June 2016, this number had surged to 26 new cases per day.
Impact and Challenges
HIV, which leads to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), is currently incurable but manageable with antiretroviral therapy (ART). The increasing rate of HIV infections in the Philippines highlights the need for enhanced public health strategies, including widespread education, regular testing, and treatment availability. However, stigma and discrimination remain significant barriers to HIV prevention and treatment.
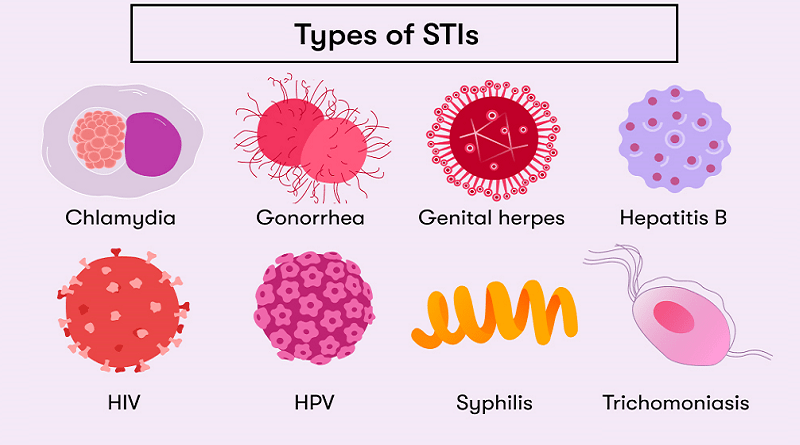
3. Common Curable STDs
Overview of Curable STDs
While HIV garners significant attention due to its incurable nature, several other STDs prevalent in the Philippines are curable with proper medical intervention. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the most common curable STDs in the Philippines are:
- Chlamydia
- Gonorrhea
- Trichomoniasis
- Syphilis
Health Implications
These STDs, if untreated, can lead to severe health issues such as:
- Neurological and cardiovascular diseases
- Ectopic pregnancies
- Infertility
- Stillbirths
- Increased susceptibility to HIV
Treatment and Prevention
These infections can be effectively treated with antibiotics. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent complications. Public health campaigns focus on promoting safe sex practices, regular screenings, and timely medical consultations to manage and reduce the incidence of these STDs.
4. Gender Disparities in STD Detection
Diagnostic Challenges in Women
STDs can affect anyone, regardless of gender, but they are often harder to diagnose in women. This is because many STDs do not show symptoms as clearly in women as they do in men. For instance, while men can often confirm their STD status with a single test, women may need a series of tests due to the internal nature of female reproductive organs.
Consequences of Delayed Diagnosis
The difficulty in diagnosing STDs in women can lead to delayed treatment, increasing the risk of severe health outcomes. Regular screenings and better diagnostic tools are essential to address this disparity. Education campaigns targeted at women can also help in recognizing subtle symptoms and seeking early medical advice.
5. Access to Testing and Treatment
Free Testing Services
In recent years, the Philippines has made significant strides in making STD testing more accessible. Several organizations and healthcare facilities offer free HIV testing. Love Yourself Centers in cities like Quezon City, Mandaluyong City, Pasay City, Manila City, and Paranaque City provide free HIV testing and counseling services. These centers also conduct seminars and programs to educate the public about STDs and their prevention.
Legal Support for Minors
A newly passed law in the Philippines allows minors to undergo HIV testing without parental consent, which is a significant step toward early detection and treatment. This law aims to reduce the barriers to testing for young people, encouraging them to seek help without fear of parental backlash.
6. Public Health Efforts and Education
Role of Education
Education plays a crucial role in STD prevention. Comprehensive sex education programs that cover safe sex practices, the importance of regular testing, and the impact of STDs can significantly reduce the incidence of these infections. Schools, community centers, and online platforms can be effective mediums for disseminating this information.
Government and NGO Initiatives
Both government and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) in the Philippines are actively involved in raising awareness about STDs. Campaigns often include distributing free condoms, providing educational materials, and organizing community events to discuss sexual health openly.
Media and Public Awareness
Media campaigns also play a vital role in changing public perceptions about STDs. By normalizing the conversation around sexual health, these campaigns help reduce stigma and encourage people to seek timely medical advice.
7. SUMMARY
The fight against STDs in the Philippines is ongoing, with significant progress made in terms of awareness, testing, and treatment. However, challenges remain, particularly in addressing stigma and ensuring equitable access to healthcare. Continued efforts in education, public health initiatives, and supportive legislation are crucial to reducing the prevalence and impact of STDs in the country.
By fostering an environment of openness and support, the Philippines can make substantial strides in managing and eventually reducing the burden of STDs. Individuals, communities, and the government must work together to achieve this goal.
Sources
- Department of Health. Stat of the Month. Retrieved from DOH. When in Manila.
- List of Clinics in the Philippines that Offer Free Testing. Retrieved from When in Manila.