Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) , causes , symptoms and treatment
Urinary Tract Infection ( also called UTI) , means infection of any part of the urinary system , which is made of 2 kidneys , 2 ureters , bladder and ends into the ureters to the outside. Urinary Tract Infection usually starts at the urethra or bladder. It may extend to other parts of urinary tract including the kidneys. Usually curable using antibacterial. Laboratory tests are required for proper diagnosis. if not treated , the condition could be dangerous.
Types Urinary Tract Infection and symptoms
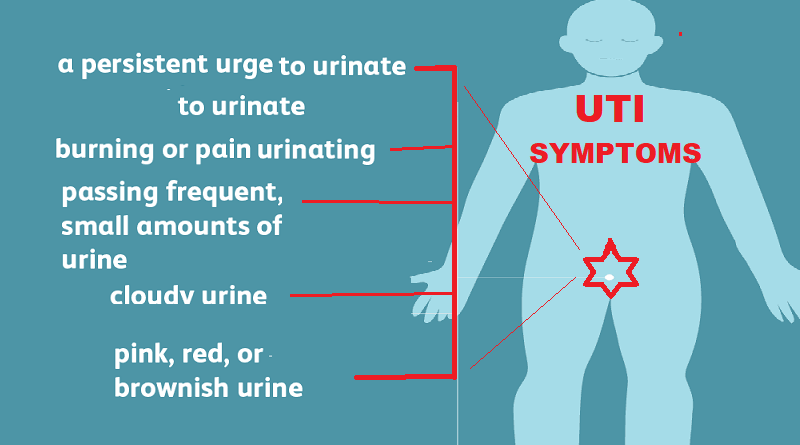
Patient usually present with pain , urination problems with or without fever. Mild cases may show no symptoms , while severe infections may be dangerous , and may require hospitalization. Symptoms of UTI vary between different types of the disease. Some of the commonly reported symptoms include the following:
- Urination problems: Patient may may present with one or more of the following urine symptoms:
Burning urination (pain during urination) , Frequent urination , urgency and incomplete voiding. Blood in urine.
Cloudy, dark, or strange or strong-smelling urine, mixed with blood in some cases - Pain: Lower body pain
in the back or lower abdomen , Pelvic pain - General symptoms (non urinary tract):
– Tiredness
– Fever and/or chills
– Nausea and/or vomiting - types of UTI depends on the infected part. So we have kidneys infection (acute pyelonephritis) , bladder (cystitis) and Urethra (urethritis).
| Type of UTI | Signs and symptoms |
|---|---|
| Kidneys (acute pyelonephritis) | Present with back pain or side pain , High fever and Nausea and Vomiting |
| Bladder (cystitis) | Pelvic and Lower abdomen pain , Frequent painful urination and Blood in urine |
| Urethra (urethritis) | Mainly painful urination and discharge |
Causes of urinary Tract Infection
Bacteria are the most common cause of UTIs , but it can be caused by fungi which is rare. The most common cause is E. coli bacteria, which live in the bowel. There many factors increasing chance of getting UTI , like the following:
- drinking less fluids than required.
- Not urinating intentionally for long periods , being busy or for any other reason.
- When the flow of urine is blocked by conditions like tumors , stones , enlarged prostate.
- Suppressed body immunity in conditions like Diabetes and others.

Diagnosis of UTI
The following are the common tests and procedures used for diagnosis:
- Urine analysis (FUA): To check for the presence of pus cells and bacteria. Cloudiness , White blood cells , Bacteria, yeast or parasites can indicate infection.
- Urine culture: To check for the exact type of organism causing infection , which is usually E.coli.
- Cystoscopy: To view the inside of the urethra and urinary bladder.
- CT scan of the abdomen is performed to check presence any abnormalities in the urinary tract.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdomen provides a complete image of urinary tract.
Treatment of UTI
UTI is is treated by Antibiotics to fight bacteria. They can be taken orally. Intravenous administration of antibiotics is recommended in severe cases.
- Sources:
- https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/urinary/conditioninfo/causes
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions
- Urinary Tract Infections: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment (clevelandclinic.org)
- Bacterial infections
- 💬 Chat with Us:
You can easily reach Helal Medical via WhatsApp (+63 966 974 1609), Facebook Messenger, or by clicking the chat icon at the lower right corner of our website HelalMedical.com.