Testicular Diseases: An Introduction
The testicles are a crucial part of the male reproductive system, with two of them situated in the scrotum. They play an important role in producing sperm and hormones that regulate male sexual development. While minor problems with the testicles can occur, such as pain, there are also significant diseases that can affect them. In this article, we will discuss the most common testicular diseases that men can face, their causes, and symptoms.
Testicular Pain
Testicular pain is one of the most common symptoms of testicular diseases, and it can indicate a minor injury or a serious problem. The pain may be the result of various causes, including testicular torsion, epididymitis, and sexually transmitted infections. Ignoring the pain can lead to irreparable damage to the testicles and scrotum. In some cases, the pain may be accompanied by discomfort in the abdomen or groin.
Common Testicular Diseases
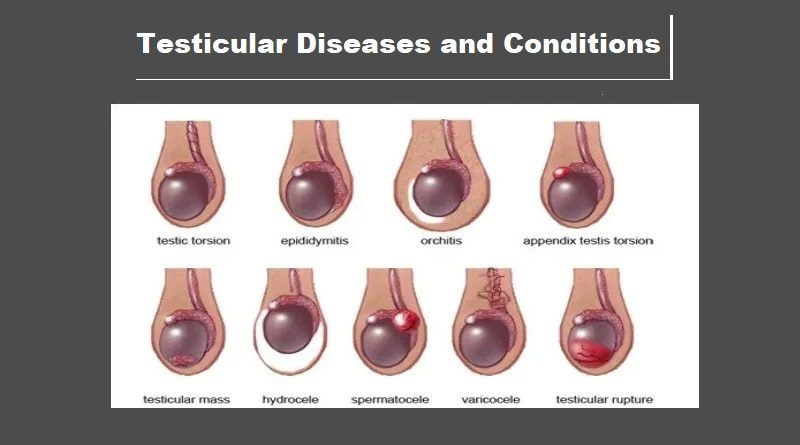
- Epididymitis: This condition is caused by inflammation or infection of the testicles and is often a result of a sexually transmitted infection. Symptoms include moderate to severe pain, swelling in the testicles or scrotum, fever, nausea, and vomiting.
- Testicular Torsion: This is a severe condition that requires immediate medical attention. Torsion occurs when the spermatic cord twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicles. If treatment is delayed for more than six hours, significant damage to the testicle can occur.
- Varicocele: This is a swelling of the veins in the scrotum, similar to varicose veins in the legs.
- Undescended Testicle: This occurs when a testicle does not descend into the scrotum.
- Hydrocele: This condition results in fluid accumulation around the testicles, causing swelling of the scrotum. It usually does not cause pain and does not require treatment.
- Spermatocele: This is fluid in the testicles.
- Testicular Cancer: This occurs when abnormal cells grow in the testicles.
Other Diseases that Can Cause Testicular Pain
- Inguinal Hernia
- Kidney Stones
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of testicular diseases typically involves a physical examination, ultrasound, and blood tests. In some cases, a biopsy may also be needed to confirm the diagnosis. It is important to seek medical attention as soon as symptoms arise to ensure an accurate and prompt diagnosis and receive the necessary treatment.
Treatment of Testicular Diseases
Treatment for testicular diseases depends mainly on the specific cause of the condition and its severity. Some common treatment lines include:
- Lifestyle changes: Lifestyle changes are the best starting treatment for most of the diseases, including testicular diseases. They include quitting smoking, start losing excess weight, and reducing stress, which can help improve symptoms and cure.
- Antibiotics: For conditions such as epididymitis, which is an infection, so antibiotics can be prescribed to treat.
- Medications: For conditions such as varicocele, medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms.
- Surgery: For conditions such as testicular torsion, where surgery may be needed to correct the problem and restore blood flow to the testicle. Other conditions include hydrocele, Varicocele, Undescended Testicle, Hydrocele and cancer may need surgery.
- Radiation therapy: For testicular cancer, radiation therapy may be used to destroy cancer cells and prevent the spread of the disease.
SUMMARY
The testicle is a vital male reproductive organ. Common testicular diseases include epididymitis, varicocele, undescended testicle, hydrocele, torsion of the testicle, testicular cancer, and erectile dysfunction. Symptoms include pain, swelling, fever, and sexual dysfunction. Testicular diseases can cause significant discomfort and harm if not treated promptly. Understanding the common causes, symptoms, and diseases is crucial in ensuring that men receive proper treatment and care.