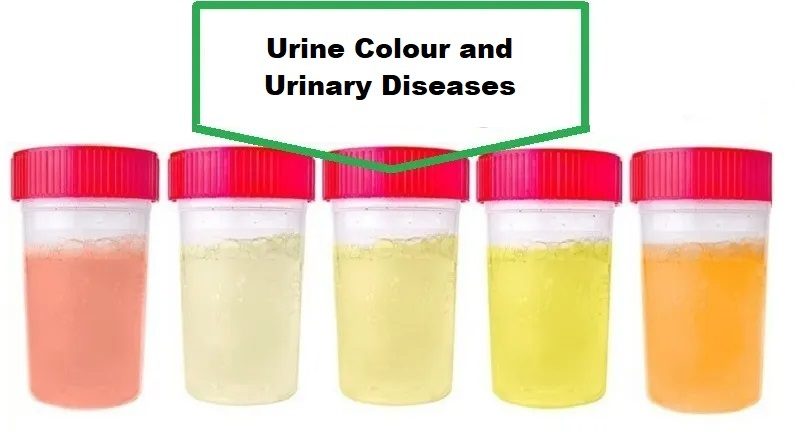
Urine Color: What Does It Mean?
Urine Color, which is normally yellow, varies depending on some factors such as the amount of water, certain medications and foods, and underlying medical conditions. In this article, we will discuss the normal range of urine colors, what different colors indicate, and the impact of medications on urine color.
Normal Urine Color Range:
The normal color of urine is yellow, and the degree of yellowing varies based on the amount of urochrome and water in the urine. The more water there is, the lighter the color will be. The normal range of urine colors is from pale yellow to dark yellow.
| Normal Color | Description |
|---|---|
| Yellow | The normal color of urine ranges from pale yellow to dark yellow, as a result of a pigment called urochrome. |
Colors of Urine Indicating a Medical Condition:
Here are some colors of urine that may indicate an underlying medical condition:
- Cloudy or Foamy Urine: Cloudy or foamy urine may indicate urinary tract infections, chronic diseases, kidney diseases, or dehydration.
- Dark Brown Urine: Dark brown urine can result from eating certain foods, such as beans and rhubarb, and from taking certain medications, including metronidazole and nitrofurantoin.
- Red or Pink Urine: Red or pink urine may indicate the presence of blood in the urine, which is a symptom of hematuria. It may also result from eating certain fruits like beets, rhubarb, and berries.
- Orange Urine: Orange urine can result from dehydration or bile diseases caused by problems in the bile ducts or liver.
- Blue or Green Urine: Blue or green urine may result from consuming food dyes or certain medications, or from urinary tract infections caused by a bacterium called Pseudomonas.
| Color Change | Cause |
|---|---|
| Clear, watery color | Drinking a large amount of water |
| Amber yellow to reddish yellow | Normal, due to the presence of urochrome. Can also result from excess B vitamins in the bloodstream |
| Red or pink | Eating fruits with pink tints (such as beets, rhubarb, and berries) or pathological causes such as blood in the urine or serious diseases |
| Orange | Dehydration or diseases of the bile ducts, liver, or refractory anemia |
| Blue or green | Food dyes or dyes used in medical tests, or urinary tract infections |
| Dark brown | Dehydration, consumption of certain foods or medications |
| Cloudy urine | Can occur due to urinary tract infections, chronic diseases, kidney diseases, or dehydration |
| Cloudy urine with foam or bubbles | Can be a symptom of serious health conditions such as Crohn’s disease or diverticulitis, and may also occur without a reason |
| Disease | Changed Color | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Hematuria | Pink, Red, Brown | Presence of red blood cells in urine |
| Dehydration | Darker, Concentrated | Not enough fluid in the body (Little water, Diarrhea or Diseases) |
| Liver Disease | Dark Brown, Tea-colored | Bile pigment in urine |
| Rhabdomyolysis | Dark Brown, Reddish-brown | Muscle damage releases muscle fibers into bloodstream |
| Porphyria | Dark Purple, Dark Brown | Genetic disorder of heme |
| Food or Drugs | Red, Pink, Orange-red, Yellow-orange | Colored foods and drugs can change the color of urine |
Impact of Medications on Urine Color:
Here are some examples of medications that can change the color:
- Iron-containing medicines
- Methocarbamol
- Flagyl metronidazole
- Chloroquine
- Methyldopa
- Amitriptyline and tryptizole
- Chlorzoxazone
- Rifampicin
- Sulfasalazine
- Warfarin
- Ibuprofen
- Phenytoin
| Medications That Change Urine Color | Description |
|---|---|
| Dark or light brown urine | Iron-containing medicines, methocarbamol, Flagyl (metronidazole), chloroquine, methyldopa |
| Blue-green | Amitriptyline and tryptizole tablets |
| Yellowish-orange | Chlorzoxazone, rifampicin, sulfasalazine, warfarin |
| Scarlet | Ibuprofen, phenytoin |
SUMMARY
The color of urine varies based on different factors, including the amount of water, certain medications and foods, and underlying medical conditions. If you notice a change in the color of your urine, it is best to consult a doctor to rule out any underlying health issues.
Urine color changes can indicate health conditions, including infections, dehydration, liver issues, and side effects of medications. Normal color ranges from pale yellow to amber. Changes can also result from foods or dyes.