Diagnosis of Gonorrhea infection , What are the available tests?
Last Updated on 02/09/2026 by Helal Medical
Some infected persons, men and women, may miss the diagnosis of gonorrhea, as they may not have any symptoms. So, it is important for any person exposed to infection undergo for diagnosis of Gonorrhea infection. Otherwise, it is easily diagnosed when infected person shows symptoms.
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which is easily spread. It spreads, mainly, through sexual intercourse, due to contact with body fluids, vaginal, oral, or anal sex, of infected persons. Pregnant women can also transmit the infection to the fetus or to the newborn during childbirth.
Diagnosis of Gonorrhea by symptoms
What are the symptoms of gonorrhea, in men and women?
1. Discharge: Greenish yellow or whitish discharge from the vagina (in females) & penis (in males)
2. Genitals are painful and swollen: the vulva in females & testicles in males
3. Burning urination
4. Eye infection: Conjunctivitis (redness, itchiness in eyes)
5. Throat infection: Burning in the throat and Swollen glands in the throat (due to oral sex)
6. Bleeding between periods in females
7. Spotting after intercourse in females
8. Pelvic inflammatory syndrome: Lower abdominal or pelvic pain in females
Gonorrhea symptoms in men
Some men infected with gonorrhea, but may have no symptoms at all.
Men who do have symptoms, may have:
A burning sensation when urinating;
A white, yellow, or green discharge from the penis;
Painful or swollen testicles (although this is less common).
Gonorrhea symptoms in women
Most women with gonorrhea do not have any symptoms. Even when a woman has symptoms, they are often mild and can be mistaken for a bladder or vaginal infection. Women with gonorrhea are at risk of developing serious complications from the infection, even if they don’t have any symptoms.
Symptoms in women can include:
Painful or burning sensation when urinating;
Increased vaginal discharge;
Vaginal bleeding between periods.
Rectal infection in men and women
Rectal infections may either cause no symptoms or cause symptoms in both men and women that may include:
Discharge; Anal itching; Soreness; Bleeding; Painful bowel movements.
By laboratory Tests for Gonorrhea
Samples to test for Gonorrhea are taken from affected areas. Transport media are required to transport specimens to the laboratory, unless transfer is immediate. Samples can be obtained from: the blood – a skin lesion – fluid from the joints – the cervix – the throat – the anus – the urethra.
There are three available tests to diagnose gonorrhea, each has its benefits and limitations. A newer technology, called the nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT), can provide genetic evidence of infection.
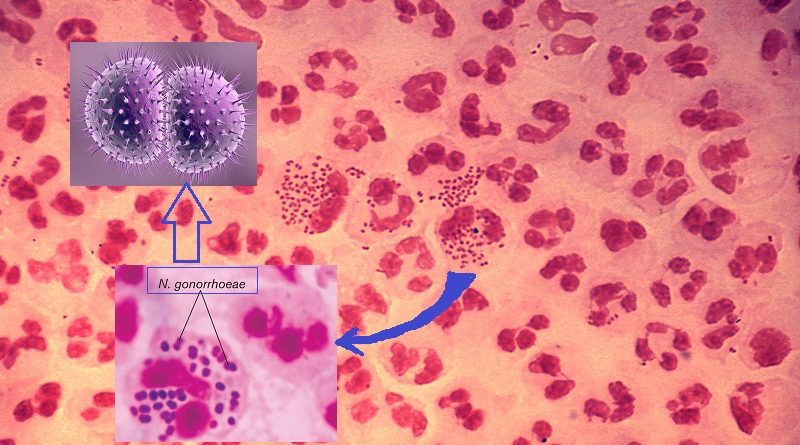
1- Gram staining method (the old routinely used method for diagnosis), but in this case sensitivity does not reach 50% for men with asymptomatic urethritis, or from cervical or rectal samples.
– Direct smear for Gram stain of urethra and cervical specimens to see Gram negative intracellular diplococci , which is more sensitive in men.
2- The isolation of N. gonorrhoeae by culture is the standard laboratory test for diagnosis. Culture is done using Thayer-Martin or other selective medium. Isolates are identified by sugar fermentation of glucose only (N. Gonorrhea does not ferment maltose or sucrose) or by Agglutination test.
3- Nucleic acid amplification techniques (recently introduced), based on PCR are faster, similar sensitivity to culture, but with greater specificity.
Sample Required for Gonorrhea Test?
For women: vaginal swabs are used to test for genital gonorrhea. A sample of cells or fluid to be collected from the vagina.
For men: A swab sample to be collected from the urethra.
Urine sample: can be collected to test both men and women.
A sample from other areas: such as the rectum, throat or eye.
Gonorrhea Test results
Positive test: indicates the presence of gonorrhea infection that requires treatment.
Negative test: means that there is no evidence of infection at the time of the test. So, it is important to reapeat the test if you were at high risk of infection.
Sexual partner: should be tested and treated , when one of them is positive.
Who should get tested?
- All sexually active women younger than 25 years should be tested for gonorrhea and chlamydia every year. Women 25 years and older with risk factors such as new or multiple sex partners or a sex partner who has an STD should also be tested for gonorrhea and chlamydia every year.
- At-risk pregnant women should also be tested for chlamydia and gonorrhea starting early in pregnancy. Testing should be repeated as needed to protect the health of mothers and their infants.
- All sexually active gay and bisexual men should be tested at least once a year for syphilis, chlamydia, and gonorrhea. Those who have multiple or anonymous partners should be tested more frequently for STDs.
- Anyone who has unsafe sex or shares injection drug equipment should get tested for HIV at least once a year.
Sources:
– https://www.cdc.gov/std/gonorrhea/stdfact-gonorrhea-detailed.htm
– https://www.cdc.gov/std/prevention/screeningreccs.htm
– Gonorrhea. (2015): www.niaid.nih.gov/diseases-conditions/gonorrhea
– Gonorrhea. (2019): womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/gonorrhea
– https://www.verywellhealth.com/how-gonorrhea-is-diagnosed-3132752
– https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/gonorrhoea/diagnosis/
– https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/gonorrhea-test/
Read More:
- The Treatment of Gonorrhea: Facing the Challenge of Antibiotic Resistance
- Gonorrhea: Transmission, Symptoms, Complications, Diagnosis, and Treatment
- 💬 Chat with Us:
- You can easily reach Helal Medical via WhatsApp (+63 966 974 1609), Facebook Messenger, or by clicking the chat icon at the lower right corner of our website HelalMedical.com.
Discover more from Helal Medical Manila
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.