HIV Western Blot Test: A Comprehensive Guide
Last Updated on 02/10/2026 by Helal Medical
HIV Western Blot (HIV WB) is a very reliable and accurate diagnostic test used to detect Human Immunodeficiency Virus infection. HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a highly contagious viral infection that affects the immune system. According to WHO, approximately 38 million people worldwide were living with HIV/AIDS in 2019. Early detection and timely treatment are crucial for the effective management of HIV.
In this article, we will discuss what is this Test, its interpretation, and its significance.
What is HIV Western Blot Test?
It’s a confirmatory test used to detect HIV antibodies in the blood, done after getting a positive screening test. It is a highly sensitive and specific test that can detect. accurately, the presence of specific antibodies to HIV proteins. After a positive result by a screening test for HIV, such as ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) or rapid test, It’s recommended to confirm by (HIV WB) . (SOURCE)
Procedure of HIV Western Blot Test:
The procedure involves the following steps:
- Blood Sample Collection:
From the patient’s arm using a needle and a syringe. - Processing of Blood Sample:
The blood sample is sent to the laboratory for testing. - Western Blotting:
In a specialized laboratory, the processed blood sample is subjected to Western Blotting, which involves separating the proteins, (including antibodies), present in the sample using a gel electrophoresis technique. The separated proteins are then transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. - Addition of Antibodies:
The nitrocellulose membrane is then incubated with HIV-specific antibodies. If HIV antibodies are present in the blood sample, they will bind to the specific antibodies on the nitrocellulose membrane. - Detection of Antibodies:
The presence of HIV antibodies is detected using a colorimetric or chemiluminescent reaction. A positive result indicates the presence of HIV antibodies, while a negative result indicates the absence of HIV antibodies.
Interpretation of (HIV WB) :
- Positive Result:
A positive result indicates the presence of HIV antibodies in the blood sample. However, a positive result on the (HIV WB) does not confirm the diagnosis of HIV infection. It is recommended to do further confirmatory tests, such as PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) or viral load test, to confirm the diagnosis. - Negative Result:
A negative result indicates the absence of HIV antibodies in the blood sample. A negative result on the Western Blot Test confirms the absence of HIV infection.
Significance of the Test:
This Test is highly accurate to confirm the diagnosis of HIV infection. It’s used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests, such as ELISA or rapid HIV test, to confirm the diagnosis of HIV infection. The test is also used to detect HIV infection in newborns born for HIV-positive mothers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q. What is the accuracy of HIV Western Blot Test?
A. It is a highly sensitive and specific test with an accuracy rate of more than 99%.
Q. How long does it take to get the results of the Test?
A. The results usually take 1-2 weeks to become available.
Q. Is (HIV WB) expensive?
A. The cost varies depending on the location and laboratory.
SUMMARY
- The Western Blot test is a blood test that is typically used to confirm a positive HIV diagnosis.
- During the test, a small sample of blood is taken and it is used to detect HIV antibodies, not the HIV virus itself.
- It separates the blood proteins and detects the specific proteins (called HIV antibodies) that indicate an HIV infection.
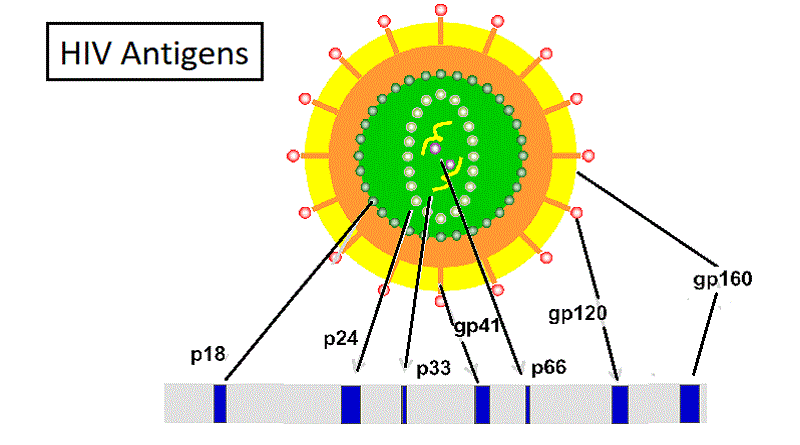
- The test looks for antibodies including 3 proteins from the HIV envelope: gp41, and gp120/gp160.
- This test is used as a second-step diagnostic tool after an initial ELISA test comes back positive for HIV antibodies.
- The test may take 1-5 days to receive results.
SOURCES
[1] https://www.healthline.com/health/hiv/western-blot-test
[2] https://stanfordhealthcare.org/medical-conditions/sexual-and-reproductive-health/hiv-aids/diagnosis/western-blot-test.html
[3] https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/testing/laboratorytests.html
Read More About HIV:
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus: Top HIV FAQstop-hiv-faqs-updated-2023. Top HIV FAQs, Transmission, prevention and Treatment
- Mar 2, 2023
- HIV infection risk, who are the most vulnerable? Main ways of HIV infection.
- Sep 21, 2021
- HIV Western Blot Test: A Comprehensive Guidehiv-western-blot-test-a-comprehensive-guide. rapid HIV test. The test is also used to detect HIV infection. HIV Western Blot (HIV WB) is a very reliable and accurate diagnostic test.
- Mar 22, 2023
- HPV tests: A Guide to Screening and Preventionhpv-tests-a-guide-to-screening-and-prevention
- Jan 17, 2023
Discover more from Helal Medical Manila
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.