Impotence Erectile Dysfunction: Causes, Complications, and Management
Erectile dysfunction (ED), commonly known as impotence, is a condition that affects a man’s ability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. It is an issue that can significantly impact a man’s life and relationships. This comprehensive guide explores the definition, causes, complications, and updated management options for erectile dysfunction.
What is Impotence Erectile Dysfunction?
It is the persistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. It is important to differentiate between occasional erectile difficulties, which can occur due to stress or temporary health issues, and chronic ED, which is a persistent problem that requires medical attention.
Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
Impotence or Erectile Dysfunction: Causes, Complications, and Management is due to a variety of causese that can be categorized into physical, psychological, and lifestyle factors. Understanding these causes is important for effective management and treatment.
Physical Causes
- Cardiovascular Diseases:
Conditions like atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) can reduce blood flow to the penis, making it difficult to achieve an erection. - Diabetes:
High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to ED. - Neurological Disorders:
Diseases such as Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and spinal cord injuries can interfere with the nerve signals responsible for erections. - Hormonal Imbalances:
Low levels of testosterone or other hormonal imbalances can contribute to ED. - Medications:
Certain medications, including antidepressants, antihypertensives, and prostate cancer treatments, can cause the condition as a side effect. - Chronic Kidney Disease:
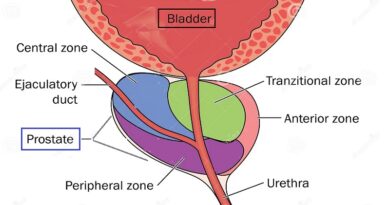
This condition can affect overall health and sexual function. - Prostate Issues:
Conditions such as prostate cancer or an enlarged prostate can impact erectile function.
Psychological Causes
- Stress: High levels of stress can affect sexual performance.
- Anxiety, particularly performance anxiety, can interfere with erections.
- Depression can reduce sexual desire and lead to ED.
- Relationship Problems: Poor communication, conflicts, or lack of intimacy with a partner can contribute to erectile difficulties.
Lifestyle Factors
lifestyle factors that can impact overall health and sexual function. Here are some key lifestyle factors contributing to ED:
- Smoking can damage blood vessels and restrict blood flow to the penis.
It is a major risk factor for ED due to its detrimental effects on blood vessels. The nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes can damage the lining of blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the penis. This impairment of blood flow is critical since erections rely on the ability to increase blood flow to the penile tissues.
Smoking causes arterial narrowing and reduced blood supply, which can lead to chronic erectile difficulties. - Alcohol Consumption:
While moderate alcohol consumption might not impact erection, excessive intake can lead to ED. Chronic alcohol use can damage the liver, nerves, and other tissues, which can affect the hormonal balance necessary for erections.
Alcohol affects the central nervous system, altering the brain’s ability to respond to sexual stimulation. Over time, it can also cause hormonal imbalances that further impede erectile function. - Drug Use:
Recreational drugs, including marijuana, cocaine, and amphetamines, can negatively impact sexual function. These substances can interfere with the nervous system and blood flow, leading to difficulties in achieving and maintaining an erection. - Obesity:
Being overweight or obese is closely linked to ED. Excess body fat can lead to cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and hormonal imbalances, all of which are risk factors for ED. Obesity also increases inflammation and oxidative stress, further damaging blood vessels and nerves. - Lack of Physical Activity:
A sedentary lifestyle can lead to poor cardiovascular health, obesity, and reduced blood flow, all contributing to ED. Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining healthy blood vessels and improving overall cardiovascular health.
Physical inactivity can lead to weight gain, reduced testosterone levels, and poor blood circulation, making it difficult to achieve and maintain an erection.
Types and Degrees of Erectile Dysfunction / Impotence
ED can manifest in various forms and severity levels. Understanding the different types and degrees is important for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Types of Erectile Dysfunction
- Primary ED: A man has never been able to achieve or sustain an erection
It is often caused by psychological factors, congenital conditions, or severe physical health issues. - Secondary ED:
More common than primary ED, this occurs in men who previously had normal erection but now face difficulties. It is often related to physical conditions, lifestyle factors, or psychological issues. - Situational ED:
This type occurs only in specific situations or with certain partners. It is typically linked to psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, or relationship issues.
Degrees of Erectile Dysfunction / Impotence
- Mild ED:
Men with mild ED may occasionally experience difficulties in erection. These episodes are infrequent and may not significantly impact their sexual satisfaction. - Moderate ED:
Men with moderate ED have more consistent difficulties with erections, often needing some form of treatment to achieve satisfactory sexual performance. - Severe ED:
It is characterized by the complete inability to have an erection. This degree of ED usually requires more intensive treatments, such as medications or surgical interventions.
Complications
It can lead to various complications that affect both health and family life.
Health Complications
- Cardiovascular Health: ED can be an early warning sign of cardiovascular diseases. Those men are at higher risk for heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular conditions.
- Mental Health: Chronic ED can lead to low self-esteem, depression, and anxiety, significantly impacting mental well-being.
- Overall Quality of Life: Persistent erectile dysfunction can affect overall quality of life, leading to dissatisfaction and distress.
Family and Relationship Complications
- Marital Strain: Erectile dysfunction can strain relationships, leading to conflicts and communication issues between partners.
- Reduced Intimacy can lead to a decrease in intimacy and sexual satisfaction, affecting relationship dynamics.
- Emotional Distress: Both partners may experience emotional distress, frustration, and feelings of inadequacy.
Updated Management Options
Management involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and psychological support. Here are some of the updated management options available:
Lifestyle Modifications
- Healthy Diet: Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can improve overall health and reduce ED symptoms.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity improves blood circulation, reduces stress, and helps maintain a healthy weight.
- Quit Smoking: Stopping smoking improves blood flow and overall cardiovascular health.
- Limiting Alcohol can improve erectile function.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress and anxiety.
Medical Treatments
The condiyion can be challenging, but various medical treatments are available to help manage it. These treatments range from oral medications to more invasive surgical options. Here’s a guide to the medical treatments available:
Oral Medications: Phosphodiesterase Type 5 (PDE5) Inhibitors
- Sildenafil (Viagra): Often the first-line treatment for ED, sildenafil helps increase blood flow to the penis by inhibiting the enzyme PDE5.
- Tadalafil (Cialis): Known for its longer duration of action, tadalafil can last up to 36 hours, providing a larger window for sexual activity.
- Vardenafil (Levitra): Similar to sildenafil, vardenafil is another PDE5 inhibitor with a slightly different chemical structure, offering an alternative for those who may not respond to other medications.
- Avanafil (Stendra): A newer PDE5 inhibitor, avanafil has a rapid onset of action and fewer side effects, making it a popular choice.
How They Work:
PDE5 inhibitors work by relaxing the blood vessels in the penis, allowing increased blood flow during sexual arousal. These medications require sexual stimulation to be effective.
Side Effects:
Common side effects include headaches, flushing, nasal congestion, and in some cases, visual disturbances. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider to ensure these medications are safe, especially for men with cardiovascular conditions.
Hormone Therapy: Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
Injections: Testosterone injections can be administered by a healthcare provider to boost low testosterone levels.
Patches and Gels: Topical applications of testosterone can be used daily to maintain hormone levels.
Implants: Small pellets can be implanted under the skin, releasing testosterone over several months.
Injection Therapy: Alprostadil
- Intracavernosal Injections: Alprostadil is injected directly into the side of the penis, causing an erection by widening blood vessels.
- Combination Therapy: Sometimes, alprostadil is combined with other medications like phentolamine and papaverine for a stronger effect.
- How It Works: Alprostadil works by relaxing smooth muscle tissue and increasing blood flow to the penis, resulting in an erection.
- Side Effects: Pain at the injection site, prolonged erections (priapism), and scarring. Proper training on injection technique is essential to minimize risks.
Vacuum Erection Devices:
- How They Work: A VED consists of a plastic tube placed over the penis, creating a vacuum that draws blood into the shaft. Once an erection is achieved, a constriction ring is placed at the base of the penis to maintain the erection.
- Advantages: Non-invasive and can be used as needed. It’s an option for men who prefer not to take medications or cannot take them due to medical reasons.
- Side Effects: Bruising and discomfort.
Surgical Treatments: Penile Implants
- Inflatable Implants: These consist of a pump placed in the scrotum and inflatable cylinders in the penis. The man can inflate the device to achieve an erection.
- Semi-Rigid Rods: Flexible rods are implanted in the penis and can be manually adjusted for erection.
- How They Work: Penile implants provide a permanent solution for severe ED. They allow men to control when and how long they have an erection.
- Side Effects: Infection, mechanical failure, and dissatisfaction with the device. Surgery and recovery can also be challenging.
Vascular Surgery:
In cases where ED is caused by vascular issues, surgery to repair or unblock blood vessels can restore proper blood flow to the penis. Side effects such as infection, bleeding, and the possibility of not achieving the desired result. This option is typically reserved for younger men with specific vascular problems.
Psychological Support
- Counseling: Therapy with a psychologist or counselor can address underlying psychological issues contributing to ED.
- Sex Therapy: Sex therapists can help couples improve communication and intimacy, reducing the impact of ED on the relationship.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and shared experiences with others facing similar challenges.
Emerging Treatments and Future Directions
Research into new treatments for erectile dysfunction continues to advance, offering hope for more effective and less invasive options in the future. Some emerging treatments include:
- Low-Intensity Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (LI-ESWT): This non-invasive treatment uses shockwaves to improve blood flow to the penis and promote tissue regeneration.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy involves injecting the patient’s own platelet-rich plasma into the penis to stimulate tissue growth and improve erectile function.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Research into stem cell therapy for ED is ongoing, with the potential to regenerate damaged tissues and restore erectile function.
- Gene Therapy: Gene therapy aims to target and repair specific genes associated with erectile function, offering a potential long-term solution for ED.
SUMMARY
Erectile dysfunction or impotence, is a complex condition with various causes, complications, and treatment options. Understanding the underlying factors and seeking appropriate medical advice is crucial for effective management. By making lifestyle changes, exploring medical treatments, and addressing psychological aspects, men can improve their erectile function and overall quality of life. Advances in research continue to provide hope for new and innovative treatments, ensuring that men with ED have access to the best possible care.