Semen analysis explained, How to read the report?
Last Updated on 02/07/2026 by Helal Medical
Why do you need to do semen analysis?
Semen analysis can help to assess 3 important cases. It can evaluate the fertility status of a man. It can confirm the success of a vasectomy operation. It can also help in the detection of infection. Male fertility can be assessed from the quantity and quality of sperm. Pus cells and red blood cells indicate infection in the male genital organs. Absence of sperm means success of vasectomy.
How is semen analysis done?
To do semen test, you need to submit a sample of your semen to the laboratory. The result may be ready in about 4 hours after the semen sample is delivered to the laboratory.
How to collect the semen sample?
Semen can be collected at 2 sites. You can collect it at the laboratory itself or at home. Then deliver it to the laboratory within 30 to 60 minutes. Collecting the sample at the laboratory is preferred. This ensures quick submission without delay. Prompt submission is important to calculate the liquefaction time.
Semen analysis is an easy test. The results are delivered quickly. Therefore, it is usually the first to be requested for couples complaining of infertility or delayed pregnancy.
How useful is semen test?
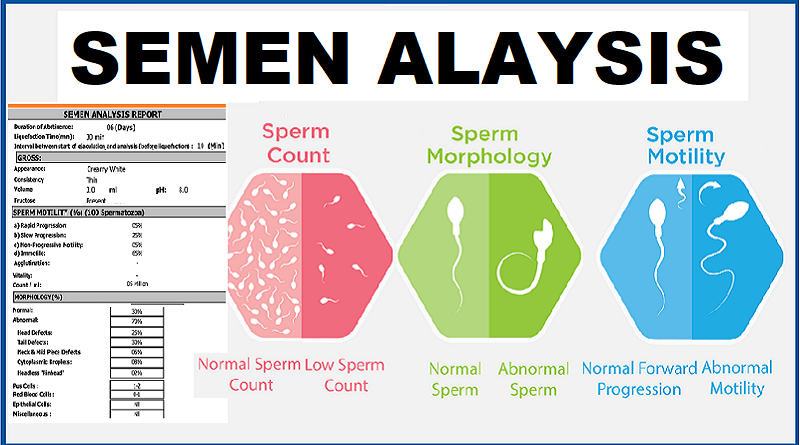
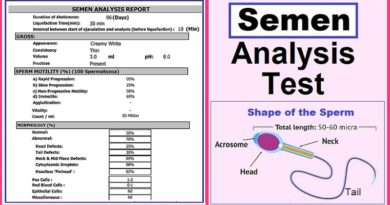
Semen test report contains many useful data. It can help assess man’s infertility and health status. This includes: sample size, liquefaction time, pH value, and date collected by microscopic examination. Microscopically, we can know several aspects. These include the number of sperm, their shape, and motility. We also examine the presence of white blood cells in the sample.
Semen analysis report
When do you need a semen analysis?
If the couple stays together for more than one year without pregnancy, it is considered a case of infertility. In this case, the man should do the semen test.
The semen analysis report is divided into several sections. Usually, it consists of three sections. The first section provides general information about the sample. The second section discusses its physical properties. These properties are observed by naked eye or using some chemical solutions. Then the third section contains the results of microscopic examination of the sample.
Section 1: semen sample general information
The data in this section includes the following:
1- Period of abstinence from sexual intercourse, which may affect the number and quality of sperm. The ideal is no sex for 3 – 7 days.
2- Collection time, which is used to calculate the liquefaction time, and to calculate the percentage of motile sperm after one hour, 2 hours, then 3 hours.
3- Liquefaction time, The normal time ranges between 20-30 minutes after ejaculation. Some bacterial diseases (infection) in the testicle may cause prolonged liquefaction time.
Section 2: Physical Properties of the semen
Appearance:
Greyish white is the normal color of semen. The color may change due to infection or presence pf red blood cells.
Sample volume – The healthy volume ranges between 2-6 ml. Infertility may occur because the sample size is small. The small size may be due to an infection or a varicocele.
Acidity level (pH): Semen is normally alkaline, between 7.2-8 , which is contributed by prostatic secretions. Excessively low or high acidity can lead to the death of sperm cells or an imbalance in their movement.
Section 3: Microscopic examination
1- Sperm count:
Normal sperm count is 15 million sperm per milliliter or more. After ligation , the success of vas ligation is measured by the absence of sperm cells, it means 0 cells. A low sperm count may suggest a production issue. This could be due to hormonal problems, an infection, inflammation, or chemical injury to the testicle.
2- Morphology:
At least 70% of the sperm are with normal shape and structure. Ill-shaped sperm cells have two heads. They may have two flagella or two tails. Sometimes, they have a short flagellum or a round head instead of being oval. The abnormal shape makes it difficult for the sperm cell to enter the egg. There are many causes for the shape problems in the sperm cells. These include chemical injury (rays) to the sperm cells. Infection can also cause these shape problems. Another cause is orchitis.
3- Motility:
Normally at least 60% of sperm are moving properly.
4- White blood cell count:
There are , normally, no white blood cells or infectious agents in the semen at all. The appearance of white blood cells indicates the presence of inflammation or infection in the testicle.
Do you have a question? please drop it down in the comments, or
Click here for (FREE ONLINE CONSULTATION)
If you suspect that you may have symptoms, Helalmedical can help, offering quick, private, and convenient testing options. You may contact us here: Facebook page.
Discover more from Helal Medical Manila
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.