Sexually transmitted Infections (STIs): A Comprehensive Guide
Last Updated on 02/09/2026 by Helal Medical
Sexually transmitted Infections (STIs) are group of infections that are spread through sexual contact. They are also called Sexually transmitted Diseases (STDs). These infections can have a variable range of symptoms, from mild to serious), and health effects, (from none to fatal). STIs are don’t affect genital organs only but also can affect other parts of the body. They are also caused by different types of microorganisms.
Whatever. it is important for individuals to practice safe sex and get tested for STDs if you were involved in unsafe sex or have any symptoms or concerns. At the public level, it’s Important to raise awareness of STIs and prevention.
I. Introduction:
- Definition: Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are infectious diseases that are spread through sex. They are caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites, affecting both men and women.
- Awareness and prevention are very important for the following reasons:
- STIs can have serious health consequences if left untreated.
- Some STIs may occur with no visible symptoms and can go undetected for long periods of time.
- Infections can be spread easily during through sexual activity.
- They can be preventable.
- It is important to know how to protect yourself from STIs and how to get tested.
- The prevention and awareness education can help reduce the spread of STIs.
II. Prevalence of Sexually transmitted Infections (STIs)
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) around the world varies depending on some factors, including geographic location, age, and sexual behavior in the community. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), there are approximately 20 million new STI cases each year in USA. Globally, there is more than 1 million new STI infections/day (World Health Organization (WHO).
Prevalence of STIs globally?
The prevalence of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) varies worldwide, globally, WHO estimates that:
Note that these statistics may not reflect the true STIs cases, as many cases go unreported.
| STI Worldwide | Estimated new cases per year |
|---|---|
| Chlamydia | 131 million |
| Gonorrhea | 78 million |
| Syphilis | 5.6 million |
| Human papillomavirus (HPV) | 290 million |
| HIV | 38 million |
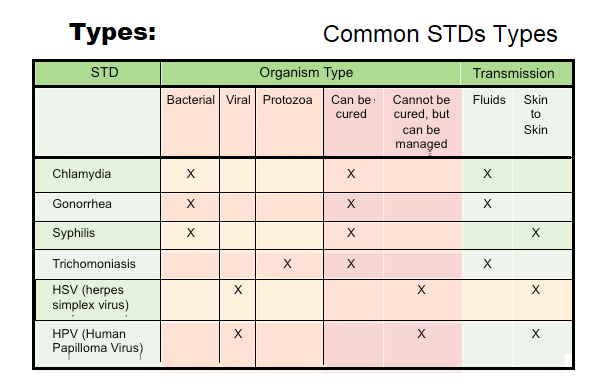
III. Types of Sexually transmitted Infections (STIs)
There are several types of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), including:
A- Bacterial STDs:
Chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis are all bacterial sexually transmitted infections (STIs). All of bacterial STIs can be easily treated with antibiotics such as Azithromycin, Doxycycline, Cefixime, or Penicillin.
| Bacterial STD | Causative Bacterium | New Cases per Year Worldwide | Symptoms | If untreated | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlamydia | Chlamydia trachomatis | 131 million | Asymptomatic or mild symptoms | PID and infertility in women | Antibiotics (Azithromycin, Doxycycline, Cefixime) |
| Gonorrhea | Neisseria gonorrhoeae | 78 million | Asymptomatic or mild symptoms | PID, infertility, DGI | Antibiotics (Azithromycin, Doxycycline, Cefixime) |
| Syphilis | Treponema pallidum | 6.3 million | Three stages with varying symptoms | Brain damage, heart disease, and death | Antibiotics (Penicillin) |
B- Viral STDs:
Viral sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are caused by viruses.
| STI | Causative Agent | Estimated new cases per year | Symptoms | Consequences if untreated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Herpes (HSV-1) | Herpes simplex virus type 1 | 3.7 billion | painful, fluid-filled blisters | can recur periodically. |
| Herpes (HSV-2) | Herpes simplex virus type 2 | 417 million | painful, fluid-filled blisters | can recur periodically. |
| HPV | Human papillomavirus | 14 million | genital warts, cervical cancer | cervical cancer |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus | 38 million | asymptomatic at early stage | AIDS |
| Hepatitis B | Hepatitis B virus | 257 million | asymptomatic at early stage | liver damage and cancer |
| Hepatitis C | Hepatitis C virus | 71 million | asymptomatic at early stage | liver damage and cancer |
IV. STIs Types- Others
C- Parasitic STDs:
There are several parasitic sexually transmitted infections (STIs) that can be transmitted through sexual contact. Here are a few examples:
| STI | Causative Agent | Estimated new cases per year | Symptoms | Consequences if untreated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trichomoniasis | Trichomonas vaginalis | 270 million | vaginal discharge, itching, painful urination | PID, Increased risk of HIV transmission |
| Pubic lice (Crabs) | Pthirus pubis | not available | itching, redness, bites on skin | none |
| Scabies | Sarcoptes scabiei | not available | itching, rash with red bumps | none |
| Giardiasis | Giardia lamblia | not available | diarrhea, abdominal cramps, gastrointestinal symptoms | none |
D- Fungal STDs:
| STI | Causative Agent | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Candidiasis (Yeast Infection) | Candida albicans | itching, burning, thick, white discharge | Over-the-counter or prescription antifungal medications |
| Jock itch | Trichophyton rubrum | itching, redness, rash in the groin area | Over-the-counter antifungal creams or sprays |
| Athlete’s foot | Trichophyton rubrum | itching, burning, redness on the skin between the toes | Over-the-counter antifungal creams or sprays |
| Ringworm (Tinea corporis) | Trichophyton rubrum | ring-shaped rash, itching, redness | Over-the-counter antifungal creams or sprays |
| Infection | Causative Agent | Transmission | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amoebiasis | Entamoeba histolytica | oral-anal contact | diarrhea, abdominal cramps, gastrointestinal symptoms | Medications |
| Chagas disease | Trypanosoma cruzi | fecal-oral route, blood transfusion, organ transplants | fever, swollen glands, rash | Medications, chronic health problems if left untreated |
Most common types of Sexually transmitted Infections (STIs)
| Common STI Name | Causative Agent |
|---|---|
| Chlamydia | Bacterial |
| Gonorrhea | Bacterial |
| Syphilis | Bacterial |
| Herpes (HSV-2) | Viral |
| HPV | Viral |
| HIV/AIDS | Viral |
| Trichomoniasis | Protozoal |
V. Transmission of Sexually transmitted Infections (STIs)
Read more about STIs transmission here!
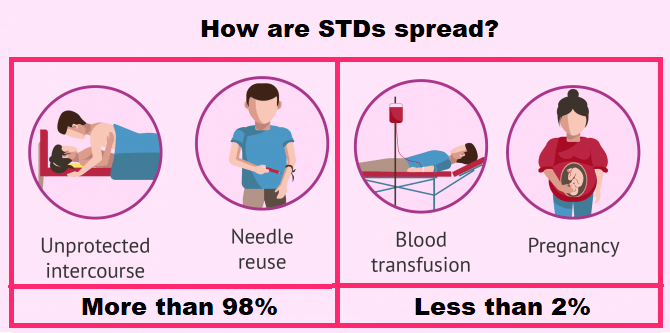
| Mode of Transmission | Examples of STDs | Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Unprotected sex | HIV, herpes, syphilis, gonorrhea | Use protection (condoms), regular STI testing |
| Sharing needles or other injection equipment | HIV, hepatitis B, hepatitis C | Use clean and sterilized needles and tools |
| Mother to baby | HIV, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, syphilis, herpes | Testing for STIs during pregnancy, antiretroviral medications, avoiding breastfeeding |
| Direct contact | Herpes, HPV, syphilis, scabies, impetigo | Avoiding skin-to-skin contact with sores or discharges |
VI. Diagnosis of Sexually transmitted Infections
A. Importance of STIs testing
There are several different methods for testing sexually transmitted Infections (STIs). They are available in medical laboratories and clinics. Home rapid tests are also available. STI testing is important for the following:
- Early detection leads to better prognosis
- Protecting partners and prevent spread
- Safe pregnancy
- Prevent complications
- Have peace of mind:
B. Types of STI Medical Tests
| Infection | Test Method | Timing of Test |
|---|---|---|
| Chlamydia and Gonorrhea | Urine test or genital swab test | Within 7-10 days of exposure |
| HIV | Blood test, oral swab test, or urine test | Within 3-4 weeks of exposure. If negative be repeated after window period for the test. |
| Herpes | Blood test or genital swab test | Within 3-7 days of symptoms appearing |
| Syphilis | Blood test | Within 3-6 weeks of exposure |
| HPV | Pap smear test or genital wart biopsy | Within 3-6 months of exposure |
Remember that some sexually transmitted infections (STIs) may be asymptomatic, therefore regular testing is highly recommended, especially when you have a new sexual partner or doing unprotected sex. Early detection and treatment of any STIs is crucial. Read more about testing and diagnosis.
VII- Treatment of Sexually transmitted Infections (STIs)
Treatment for sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) vary depending on the type of infection and patients circumstances. Some common treatment options include:
- Antibiotics for Bacterial STDs. Medications are usually taken as a single dose or a short course.
- Antiviral medications for Viral STDs.
- Topical medications for parasitic and fungal infections.
- Surgery may be necessary to remove warts or other growths of HPV or to treat complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease or testicular infections.
- Vaccines can be prevent some STIs such as Hepatitis B.
VIII- Prevention of Sexually transmitted Infections (STIs)
There are several techniques for preventing and protecting against Sexually transmitted Infections (STIs), Read more about prevention here:
X- Social impact of Sexually transmitted Infections (STIs)
The impact of stigma and discrimination on individuals with Sexually transmitted Infections (STIs) can be significant. People who have STDs may experience feelings of shame, embarrassment, and isolation, which can make it difficult for them to seek medical care or disclose their status to sexual partners. Read more here!
SUMMARY
Sexually transmitted Infections (STIs) are infections that are spread through sexual contact. They can have a range of symptoms and health effects. To prevent STDs, practice safe sex and get tested regularly. The types of STDs are bacterial, viral, parasitic, fungal and protozoan. The most common types are chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, herpes, HPV, HIV, trichomoniasis. STDs can be spread through sexual contact, sharing needles and other injection equipment, from mother to baby during childbirth or breastfeeding. Testing for STDs is important to detect and prevent the spread of infections, protect your health and future health, and provide peace of mind. Diagnosis typically involves a medical history, physical examination and laboratory tests.
Resources for further information.
There are several resources for further information on Sexually transmitted Infections (STIs):
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website provides information on the causes, symptoms, and treatment of STDs, as well as resources for testing and prevention. CDC – STD Diseases & Related Conditions
- The World Health Organization (WHO) website provides global information on STDs including facts, statistics, and recommendations for prevention and control. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) (who.int)
- The American Sexual Health Association (ASHA) website provides information on STDs, including facts, statistics, and resources for testing and treatment.
- The American Social Health Association (ASHA) website provides information on STDs, including facts, statistics, and resources for testing and treatment. STDs A to Z – American Sexual Health Association (ashasexualhealth.org)
- The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) website provides information on research related to the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of STDs. Sexually Transmitted Diseases | NIH: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
- Types of STIs: Bacterial, Viral, Fungal & Parasitic Transmitted Infections (drseb.com)
Discover more from Helal Medical Manila
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.