Understanding Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Last Updated on 02/09/2026 by Helal Medical
When it comes to personal health, certain topics may make us blush or feel uncomfortable. One such topic is urinary tract infections (UTIs). Discussing them might be uncomfortable. However, UTIs are a common condition that can affect anyone. They don’t discriminate by age or gender. In this article, we will discuss urinary tract infections. We will shed light on what they are, their causes, and symptoms. Additionally, we will talk about treatment options and preventative measures.
Understanding Urinary Tract Infections
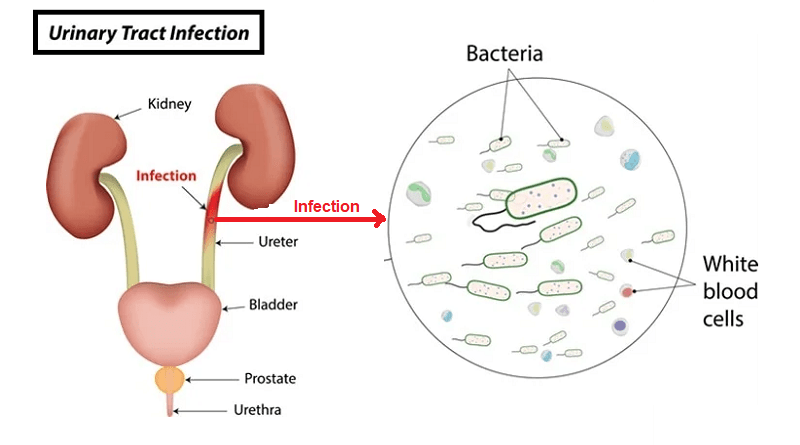
The urinary tract is a vital part of our excretory system. It is responsible for eliminating waste. It also maintains fluid balance in our bodies. A urinary tract infection begins when bacteria, usually from the digestive system, enter the urinary tract. The bacteria then multiply, leading to an infection.
UTIs can affect different parts of the urinary tract, including the bladder (cystitis), urethra (urethritis), or kidneys (pyelonephritis). Women are more prone to UTIs because they have a shorter urethra. This anatomical difference makes it easier for bacteria to enter the urinary tract. However, UTIs can occur in men as well, and they can be particularly concerning when they reach the kidneys.
Common Causes
Bacteria typically cause urinary tract infections (UTIs) when they enter the urethra. They then travel up to the bladder or other parts of the urinary tract. The most common cause of UTIs is a type of bacteria called Escherichia coli (E. coli), which normally resides in the intestines but can enter the urinary tract and cause infection. However, UTIs can also be caused by other types of bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Some common causes and risk factors for UTIs include:
- Sexual Activity:
Sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urethra, increasing the risk of UTIs, especially in women. This is commonly referred to as “honeymoon cystitis” and is more common in individuals who are sexually active. - Anatomy:
In women, the urethra is shorter. It is also closer to the anus. This structure makes it easier for bacteria to enter the urinary tract. This anatomical factor increases the susceptibility to UTIs. - Urinary Tract Obstructions:
Any condition can increase the risk of UTIs. This occurs if it obstructs or blocks the normal flow of urine. This includes conditions like kidney stones, an enlarged prostate in men, or urinary tract abnormalities. Obstructions can interfere with the complete emptying of the bladder, allowing bacteria to multiply and cause infection. - Weak Immune System:
Individuals with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to infections. This includes conditions like diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or undergoing chemotherapy. These individuals are especially vulnerable to UTIs. - Urinary Catheterization:
The use of urinary catheters involves inserting thin tubes into the bladder to drain urine. This process can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract. It also increases the risk of UTIs. - Poor Hygiene:
Inadequate personal hygiene can lead to health issues. Wiping from back to front after bowel movements can easily transfer bacteria from the anal area. This transfer facilitates movement of bacteria to the urethra. This increases the risk of UTIs. - Postmenopausal Changes:
After menopause, hormonal changes can cause changes in the urinary tract, making it more susceptible to infections. - Use of Spermicides or Diaphragms:
Certain contraceptive methods, such as spermicides and diaphragms, can increase the risk of UTIs. They may affect some individuals.
Symptoms
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) can cause a range of symptoms that vary in severity. Common symptoms of UTIs include:
- Frequent Urination:
A persistent urge to urinate more often than usual is a common symptom of UTIs. This may be accompanied by the feeling of incomplete bladder emptying. - Pain or Burning Sensation:
Pain or a burning sensation during urination is a classic symptom of UTIs. This discomfort is often felt in the urethra, the tube that carries urine out of the body. - Cloudy or Bloody Urine:
UTIs can cause changes in the appearance of urine. It may appear cloudy, have a strong odor, or contain blood. - Lower Abdominal or Pelvic Pain:
Some individuals with UTIs experience pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen or pelvic region. This pain may be mild or severe and can persist even when not urinating. - Fever or Chills:
In more severe cases, UTIs can lead to systemic symptoms such as fever, chills, and general malaise. These symptoms indicate that the infection may have spread to the kidneys and require immediate medical attention.
Treatment and Prevention
If you suspect you have a UTI, seeking medical advice is essential. A healthcare professional will conduct a physical examination. They will evaluate your symptoms. Additionally, they will perform a urine test to confirm the presence of bacteria. Antibiotics are typically prescribed to treat UTIs and are often effective in relieving symptoms within a few days. It is crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics to ensure the infection is completely eradicated.
Preventing UTIs involves adopting healthy habits. Drinking plenty of water helps flush out bacteria from the urinary tract. Practicing good hygiene is crucial. For example, wiping from front to back after using the toilet helps prevent the spread of bacteria. Empty your bladder before and after sexual activity. Avoid harsh feminine hygiene products. Wear breathable underwear. These actions can also reduce the risk of UTIs. For individuals prone to recurrent UTIs, healthcare professionals may recommend additional preventive measures. They might suggest low-dose antibiotics or other targeted strategies.
SUMMARY
Urinary tract infections might be uncomfortable and often overlooked. However, understanding their causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention is crucial for maintaining good urinary health. By debunking the stigma surrounding UTIs, we can encourage open conversations and educate individuals about this common condition. Remember, seeking timely medical attention, adopting healthy habits, and following preventive measures can help manage UTIs effectively. Knowledge is power, and in the case of UTIs, it’s the key to reclaiming comfort and well-being.
If you suspect that you may have symptoms, Helalmedical can help, offering quick, private, and convenient testing options. You may contact us here: Facebook page.
Discover more from Helal Medical Manila
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.