Epididymitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
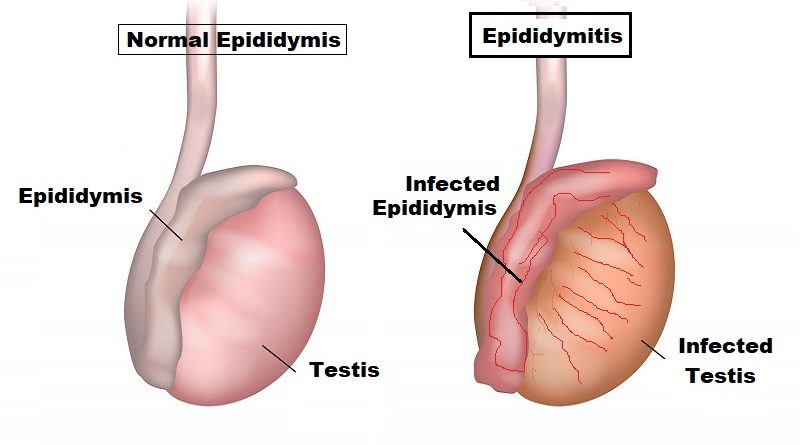
Epididymitis is a disease affecting the epididymis, which is a coiled tube located at the back of the testicle. the epididymis stores and transfers sperm to the spermatic cord. The disease, most commonly, affects young men between the ages of 20 and 45, but can occur in males of any age. The cause is a bacterial infection, including sexually transmitted diseases like gonorrhea and chlamydia.
Causes of Epididymitis
- Bacterial infections (gonorrhea, chlamydia) through sexual transmission are common causes in adults.
- In children, it can result from direct trauma or a urinary tract infection (E. coli).
- Risk factors include lack of circumcision, urinary tract diseases, multiple sexual partners, and not using condoms during sexual activity.
Symptoms
Testicular pain, fever, sensitivity in the testicle area, blood in semen, secretions from the penis, discomfort in lower abdomen or pelvis, fever, pain during ejaculation, painful urination, and painful scrotum swelling.
- Testicular pain: severe pain in the testicle is a common symptom of epididymitis.
- Fever: a high body temperature or fever is often a sign of an infection.
- Scrotal swelling: the scrotum may become swollen and tender.
- Discharge from the penis: secretions from the penis may be present in some cases.
- Urinary symptoms: pain or burning during urination, as well as an increased frequency of urination, may be present.
- Pain during ejaculation: some individuals may experience pain during ejaculation.
- Heaviness or discomfort in the lower abdomen or pelvis: individuals may feel a sense of discomfort or heaviness in the pelvic region.
Diagnosis of Epididymitis
- Clinical examination, testing for sexually transmitted infections, urine tests, and ultrasound.
- The doctor may look for enlarged lymph nodes in the groin, testicles, and prostate.
- Ultrasound can rule out testicular torsion and confirm the diagnosis of epididymitis through blood flow analysis.
Differential diagnosis of epididymitis
To reach a correct diagnosis of epididymitis, doctors must look at other conditions that have similar symptoms, like testicular pain, and rule them out. These conditions may include:
- Testicular torsion: a medical emergency in which the testicle rotates and twists on the spermatic cord, leading to decreased blood flow to the testicle.
- Prostatitis: an infection or inflammation of the prostate gland.
- Orchitis: inflammation of the testicles.
- Testicular cancer: a rare but serious condition that requires prompt medical attention.
- Urinary tract infection: an infection in the urinary tract that can cause symptoms similar to epididymitis.
- Inguinal hernia: a condition in which part of the intestine bulges through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles.
- Scrotal abscess: a collection of pus in the scrotum.
- Trauma: injury to the testicles or scrotum can cause symptoms similar to epididymitis.
| Condition | Characteristic Signs & Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Testicular Torsion | Sudden, severe pain in the testicle, swelling of the scrotum, nausea, vomiting, difficulty walking |
| Prostatitis | Pain or discomfort in the groin area, painful urination, frequent urination, pain during ejaculation |
| Orchitis | Pain, swelling and redness in one or both testicles, fever, body aches, abdominal pain |
| Testicular Cancer | A painless lump or swelling in the testicle, a heavy or aching feeling in the scrotum, discomfort or pain in the testicle or scrotum |
| Urinary Tract Infection | Painful or burning sensation during urination, frequent urges to urinate, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, pain in the lower abdomen or back |
| Inguinal Hernia | Bulge in the lower abdomen or groin area, pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen, swelling or a heavy feeling in the scrotum |
| Scrotal Abscess | Pain and swelling in the scrotum, redness and warmth, tenderness to the touch, fever |
| Trauma | Pain and swelling in the scrotum or testicles, bruising, difficulty walking or standing, blood in the semen or urine |
Treatment
- Early diagnosis and prompt treatment with antibiotics, pain relievers, and lifestyle changes is crucial to prevent damage to the testicle.
- Avoid sexual activity during treatment and treat any sexual partners to prevent re-infection.
- Follow a healthy lifestyle during and after treatment.
SUMMARY
Epididymitis is a condition that affects the epididymis and is often caused by bacterial infections. Symptoms include testicular pain, fever, and urinary problems. Prompt treatment with antibiotics, pain relievers, and avoiding sexual activity can prevent further damage to the testicles.
Key Words: Epididymitis, Bacterial Infections, Testicular Pain, Fever, Urinary Problems.
SOURCES
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases
- https://www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/